In May, I saw the announcement of a new research brief by Common Sense Advisory, which, according to its summary, would explain why companies are starting to centralize their language services. That made sense to me. In fact, it made me happy.
Not happy enough to cough up the money to purchase the study, I am afraid. But as people interested in terminology management, don’t you think that the following paragraph from the announcement sounds good? “Large organizations have begun consolidating their translation activities into internal service groups responsible for a broad range of language-related functions. This brief outlines the rationale behind and steps involved in enterprise language processing, including centralized operations, process re-engineering, automation, and content and metadata remediation.”
It sounds good, because anything else but a centralized service for prescriptive terminology management in an enterprise would be counterproductive. A centralized terminology database with a centralized service allows an entire company to contribute to and make use of the asset. According to Fred Lessing’s remar in an earlier posting, Daimler did a good job with this. Here is what they and companies, such as IBM and SAP, who have had a centralized service for years, if not decades, are getting out of it:
- Standardization: If product teams reuse terms, it leads to consistent corporate language. Documenting a term once and reusing it a million times, helps getting a clear message out to the customer and sets a company off from its competitors.
- Cost savings: The Gilbane Group puts it nicely in this presentation: “Ca-ching each time someone needs to touch the content.” It might cost $20 to set up one entry initially, but ten questions that didn’t need to be asked, might save $200 and a lot of aggravation. There are many terminology questions that come in for a major release. If I remember correctly, there were 8000 questions for a Windows Server release back when things hadn’t been centralized; many translators asked the same question or asked because they couldn’t access the database.
- Skills recycling: That’s right. It takes “strange” skills to set up a correct and complete entry. A person who does it every now and then might not remember what the meaning of a data category field, forgets the workflow, or simply can’t understand the question by a translator. And yet, entries have to be set up quickly and reliably, otherwise we get the picture painted in this posting. A centralized team, who does it all the time, refines skills further and further, and again, saves time because no questions need to be asked later.
But all that glitters is not gold with centralization either. There are drawbacks, which a team of committed leaders should plan for:
- Scale: Users, contributors and system owners all have to be on board. And that takes time and commitment, as the distance between people in the system may be large, both physically and philosophically. Evangelization efforts have to be planned.
 Cost allocation: A centralized team might be in a group that doesn’t produce revenue. As a member of terminology teams, I have worked in customer support, content publishing, product teams, and the training and standardization organization. When I had a benchmarking conversation with the Daimler team in 2007, they were located in HR. The label of the organization doesn’t matter so much than whether the group receives funding for terminology work from those groups that do generate revenue. Or whether the leadership even just gets what the team is doing.
Cost allocation: A centralized team might be in a group that doesn’t produce revenue. As a member of terminology teams, I have worked in customer support, content publishing, product teams, and the training and standardization organization. When I had a benchmarking conversation with the Daimler team in 2007, they were located in HR. The label of the organization doesn’t matter so much than whether the group receives funding for terminology work from those groups that do generate revenue. Or whether the leadership even just gets what the team is doing.
I believe that last point is what broke the camel’s back at Microsoft: Last week, the centralized terminologist team at Microsoft was dismantled. The terminologist in me is simply sad for all the work that we put in to build up a centralized terminology management service. The business person in me is mad for the waste of resources. And the human worries about four former colleagues who were let go, and the rest who were re-organized into other positions. Here is good luck to all of them!
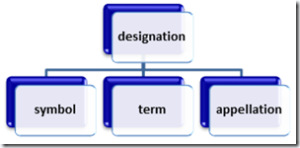 Terms represent generic concepts. They are the parent concept or superordinate to other concepts. The concept called “operating system” in English has many different subordinate concepts, e.g. Windows, Linux, or Mac OS. Many times generic concepts have native-language equivalents in other languages. Of course, a particular language may borrow a term from another language, a direct loan. But that should be a deliberate term formation method and it is just one of them, as discussed in
Terms represent generic concepts. They are the parent concept or superordinate to other concepts. The concept called “operating system” in English has many different subordinate concepts, e.g. Windows, Linux, or Mac OS. Many times generic concepts have native-language equivalents in other languages. Of course, a particular language may borrow a term from another language, a direct loan. But that should be a deliberate term formation method and it is just one of them, as discussed in  Once again, I find ISO 704 very helpful: “Technically, appellations are not translated but remain in their original language. However, an individual concept may have an appellation in different languages.” Good examples are international organizations which tend to have appellations in all languages of the member states, such as the European Union, die Europäische Union, or l’Union européenne.
Once again, I find ISO 704 very helpful: “Technically, appellations are not translated but remain in their original language. However, an individual concept may have an appellation in different languages.” Good examples are international organizations which tend to have appellations in all languages of the member states, such as the European Union, die Europäische Union, or l’Union européenne. There are actually two concepts hidden behind this name:
There are actually two concepts hidden behind this name: Naming is a big part of terminology management. In her presentation for the last DTT symposium, Beate Früh, language service manager at
Naming is a big part of terminology management. In her presentation for the last DTT symposium, Beate Früh, language service manager at