One of the main reasons we have doublettes in our databases is that we often don’t get around to doing proper terminological analysis. I was just witness to and assistant in a prime example of a team doing this analysis at the meetings of ISO TC37.
ISO TC 37 is the technical committee for “Terminology and other language and content resources.” It is the standards body responsible for standards such as ISO 12620 (now retired, as discussed in an earlier posting), 704 (as discussed here) or soon 26162 (already quoted here). This year, the four subcommittees (SCs) and their respective working groups (WGs) met in Seoul, South Korea, from June 12 through 17.
One of these working groups had considerable trouble coming to an agreement on various aspects of a standard. Most of us know how hard it is to get subject matter experts (or language people!) to agree on something. Imagine a multi-cultural group of experts who are tasked with producing an international standard and who have native languages other than English, the language of discussion! The convener, my colleague and a seasoned terminologist, Nelida Chan, recognized that the predicament could be alleviated by some terminology work, more precisely by thorough terminological analysis.
First, she gave a short overview of the basics of terminology work, as outlined in ISO 704 Terminology work – Principles and methods. Then the group agreed on the subject field and listed it on a white board. Any of the concepts up for discussion had to be in reference to this subject field; if the discussion drifted off into general language, the reminder to focus on the subject field was right on the board.
 The group knew that they had to define and name three different concepts that they had been struggling with, although lots of research had been done; so we put three boxes on the board as well. We then discussed, agreed on and added the superordinate to each box, which was the same in each case. We also discussed what distinguished each box from the other two. Furthermore, we found examples of the concepts and added what turned out to be subordinates right into the appropriate box. Not until then did we give the concepts names. And now, naming was easy.
The group knew that they had to define and name three different concepts that they had been struggling with, although lots of research had been done; so we put three boxes on the board as well. We then discussed, agreed on and added the superordinate to each box, which was the same in each case. We also discussed what distinguished each box from the other two. Furthermore, we found examples of the concepts and added what turned out to be subordinates right into the appropriate box. Not until then did we give the concepts names. And now, naming was easy.
| Step 1 | SUBJECT FIELD | ||
| Step 2 | Superordinate | Superordinate | Superordinate |
| Step 3 | Distinguishing characteristic 1 Distinguishing characteristic 2 |
Distinguishing characteristic 1 Distinguishing characteristic 2 |
Distinguishing characteristic 1 Distinguishing characteristic 2 |
| (Step 4) | Subordinate Subordinate |
||
| Step 5 | Designator | Designator | Designator |
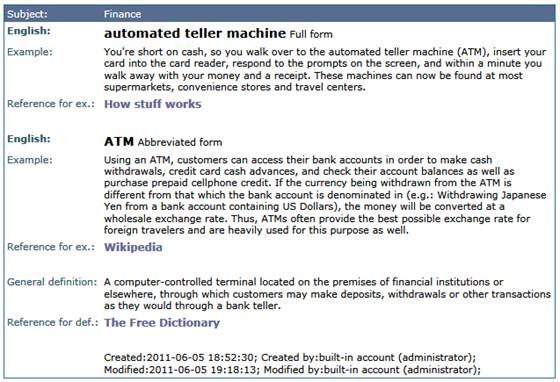
After this exercise, we had a definition, composed of the superordinate and its distinguishing characteristics as well as terms for the concepts. Not only did the group agree on the terms and their meanings, the data can now also be stored in the ISO terminology database. Without doublettes.
Granted, as terminologists we don’t often have the luxury of having 15 experts in one room for a discussion. But sometimes we do: I remember discussing terms and appellations for new gaming concepts in Windows Vista with marketing folks in a conference room at the Microsoft subsidiary in Munich. Even if we don’t have all experts in shouting distance, we can proceed in a similar fashion and collect the information from virtual teams and other resources in our daily work. It may take a little bit to become fluent in the process, but terminological analysis helps us avoid doublettes and pays off in the long run.